Prevalence and Outcome of Preterm Neonates Admitted to Neonatal Unit of a Tertiary Care Center in Western Nepal
Keywords:
Gestational Age, NICU, Preterm neonates, Neonatal UnitAbstract
Introduction: Preterm deliveries contribute to major morbidity and mortality in developing countries. They are a leading cause of admission in neonatal care units. Advances in the management have ensured better survival of preterm births, however cost, care and resource limitations influence the outcome.This study was conducted to determine the prevalence, risk factors, morbidity patterns and outcome of preterm admissions to a neonatal unit of a tertiary care center.
Methods: This was a retrospective study where all preterm admissions over a period of two years were evaluated for maternal risk factors and morbidity pattern. Outcome was measured in terms of survival rate and case fatality rate. Mann Whitney U test and Fisher's Exact test were used to see the association between various parameters and clinical outcome.
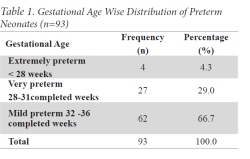
Results: Preterm admissions constituted16.48% of all neonatal unit admissions with a male to female ratio of 1.32:1. Common risk factors for preterm births were Prelabour Rupture of Membrane (31.2%) followed by Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy (15.1%) and Antepartum Hemorrhage (8.6%). Common morbidities were Sepsis (40.9%), Jaundice (28%) and Respiratory Distress Syndrome (RDS) (14%). Case fatality rate was significantly high in RDS (45.1%) and perinatal asphyxia (11.1%). Overall survival rate was 75.26%.
Conclusion: Preterm births were an important cause for admissions in neonatal unit. Sepsis, jaundice, RDS and necrotizing enterocolitis were common morbidities observed. Since clinical outcome was related to gestational age, improving antenatal care, timely interventions and early referral of high risk pregnancies to tertiary level centers might improve the survival rate.
Downloads
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
The Journal of Lumbini Medical College (JLMC) publishes open access articles under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution(CC BY) License which permits use, distribution and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.JLMC requires an exclusive licence allowing to publish the article in print and online.
The corresponding author should read and agree to the following statement before submission of the manuscript for publication,
License agreement
In submitting an article to Journal of Lumbini Medical College (JLMC) I certify that:
- I am authorized by my co-authors to enter into these arrangements.
- I warrant, on behalf of myself and my co-authors, that:
- the article is original, has not been formally published in any other peer-reviewed journal, is not under consideration by any other journal and does not infringe any existing copyright or any other third party rights;
- I am/we are the sole author(s) of the article and have full authority to enter into this agreement and in granting rights to JLMC are not in breach of any other obligation;
- the article contains nothing that is unlawful, libellous, or which would, if published, constitute a breach of contract or of confidence or of commitment given to secrecy;
- I/we have taken due care to ensure the integrity of the article. To my/our - and currently accepted scientific - knowledge all statements contained in it purporting to be facts are true and any formula or instruction contained in the article will not, if followed accurately, cause any injury, illness or damage to the user.
- I, and all co-authors, agree that the article, if editorially accepted for publication, shall be licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0. If the law requires that the article be published in the public domain, I/we will notify JLMC at the time of submission, and in such cases the article shall be released under the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver. For the avoidance of doubt it is stated that sections 1 and 2 of this license agreement shall apply and prevail regardless of whether the article is published under Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 or the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver.
- I, and all co-authors, agree that, if the article is editorially accepted for publication in JLMC, data included in the article shall be made available under the Creative Commons 1.0 Public Domain Dedication waiver, unless otherwise stated. For the avoidance of doubt it is stated that sections 1, 2, and 3 of this license agreement shall apply and prevail.
Please visit Creative Commons web page for details of the terms.



